From rookie to SEO rock star, we all need to cover our bases in terms of knowledge and practice and an updated SEO Dictionary is always of great help.
This SEO glossary includes 50 key terms that should be enough to cover basic to advanced levels, following the way a practitioner learns the basics of search engine optimization.
Terms included in the SEO Dictionary:
- Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
- Algorithm
- Anchor Text
- Authority
- Backlinks
- Black hat SEO
- Branded / Non-branded search
- Broken link
- Caching
- Canonical URLs
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift)
- Core Web Vitals
- Crawling
- E-A-T rating
- Featured snippets
- FID (First Input Delay)
- Google BERT
- Google Discover
- Google Search Console
- HTTP 1.1 protocol
- Indexing
- Keyphrase
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint)
- Meta Description
- Organic vs. Non-organic
- Page Status Codes
- Preferred Domain
- Protocol (HTTP, HTTPS, SSL)
- Query
- Redirection
- Rich Results and Rich Snippets
- Robots.txt
- Search engine PPC (Pay-Per-Click) ads
- SEM (Search Engine Marketing)
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
- SERP (Search Engine Results Page)
- SERP features
- Spider / Web Crawler
- Structured Data
- Tags
- Technical SEO
- URL
- URL structure
- User Experience (UX)
- User intent
- YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) websites
- Webmaster Tools
- White hat SEO
- XML sitemap
A
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
Accelerated Mobile Pages is a light version of a website initially created by Google as a competitor to Facebook Instant Articles and Apple News. This open-source HTML framework developed by AMP Open Source is designed to make the user experience faster for mobile visitors.
I personally tried it on several projects but came across many issues with SEO indexing, especially in multilingual websites. For speeding up a website’s loading time I would choose instead a world-class caching solution like Cloudflare.
Algorithm
In SEO, the term “algorithm” refers to a “search algorithm”: a complex structure of logical conditions created by engineers working for search engines to parse content, to process it, and to deliver the most relevant results to users’ search queries.
Currently, Google, Bing, and all search engines use multiple algorithm structures do deliver search engine results pages (SERP) based on hundreds of ranking factors.
Algorithms change, so we must differentiate an algorithm update from a new search algorithm. Every year, Google updates its search algorithm more than 1000 times, but it doesn’t change the entire algorithm, as was the case for Google Penguin algorithm and Google Panda algorithm.
Anchor Text
The Anchor Text represents the word string that is the visible part of a link. Many websites have problems with Anchor Texts because they are not set properly, specifically it is not clear what the link is about without having to click it, so I decided to include it in this SEO Vocabulary.
For example, if my partners would link my website, they should display it as Stefan Stroe.
Authority (or Domain Authority)
Authority is the score that each website receives from search engines’ algorithms based on the signals they identify in its contents (backlinks, E-A-T ratings). Domain Authority is a strategic score of utter importance, as it allows content managers to have their new content rank higher in results pages.
B
Backlinks
Backlinks are the links that your website benefits from. They can be split into two categories: internal backlinks and external backlinks. Your website needs them both for two reasons: to guide users on your website and to indicate search engines how your website’s pages relate to each other.
Internal Backlinks
They are all the links used to coss-link pages in a website. They are very important to guide both users and search engines on how to read the content (for example prompting related content).
External Backlinks
Are links that a website receives from outside (websites, social platforms, etcetera). They are extremely important as they build the ranking (domain authority) of a website. It is important to receive backlinks from important websites and platforms, which have high domain authority.
Black hat SEO
Just like the dark force in Star wars, black hat SEO is a fraudulent way of optimization that violates search engines’ usage and quality guidelines. Usually, it’s performed by website managers that intend to improve Google rankings faster than normal and for that purpose, they implement abusive or questionable techniques.
Since I totally disagree with using them, I will mention only a few: keyword stuffing, doorway pages, content automation, clickbait, link farming. Hopefully, most of these techniques are already picked up by Google Search algorithm and most websites that use them are being penalized. Read more about these techniques on Cognitiveseo.com Blog.
Broken link
It is a link that returns error 404 (not found). This could happen when there is a syntax error in the URL on your site, when the destination page has changed (for example the target website updated the page slug), or when the destination page has been deleted without applying any 3xx redirection.
Branded / Non-branded search
The queries that users type in search engines to reach a website may be branded or non-branded (including or not a specific brand name).
From a marketing strategy point of view, brand awareness is directly correlated with Branded search queries, whilst the non-branded search is related to website content that is generic and thus not associated with the brand. Non-brand search on the other hand is the holy grail of SEO, as it offers an opportunity to increase revenue by targeting new prospects.
C
Caching
Caching is a very important User Experience (UX) tool, as it makes a website to load faster by copying it in a static version on the server. A big advantage when using caching is that it lowers the processing capacity of users’ mobile browsers, making thus pages to load quicker on small devices.
In WordPress, you could use free or paid caching plugins (there are at least 5 good alternatives) but also a CDN solution.
Canonical URLs
The Canonical URL is an HTML parameter that indicates search engine crawlers which is the original version of a web page and which are duplicates. This action prevents receiving a “Duplicated content” red-flagging in Google Search Console and allows the original page to be successfully indexed.
Click-Through Rate (CTR)
It is a statistical SEO key performance indicator in the vocabulary that represents the rate at which users click a certain page listed in Google Search results.
CTR is calculated by dividing the number of clicks recorded by a certain page listed in Google Search to the total number, multiplied by 100.
This indicator is first seen in Google Search Console. For example, if a website records in 28 days 5000 clicks and 15000 views, the CTR (click-through rate) is 5000/15000*100=33%.
CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift)
It measures how much a page’s layout shifts during loading. Unlike LCP and FID which are measured in seconds, CLS has a score ranging between 0 and 1 (zero = no layout shifting; 1 = high layout shifting).
Google measures CLS for qualitative reasons (User Experience) because websites should load smoothly, without experiencing shifting sections and elements during the process.
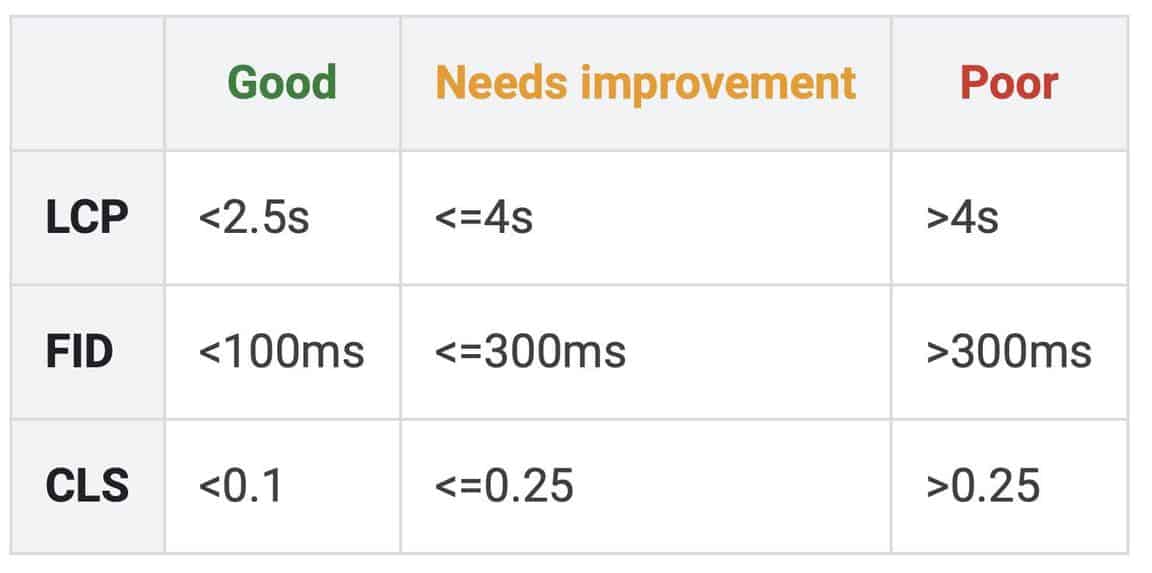
Good CLS:
- <0.1
CLS that needs improvement:
- <=0.25
Poor CLS:
- >0.25
Core Web Vitals
A set of key performance indicators gathered in a unique report, which shows how well web pages perform based on real-world usage data (which Google calls field data).
Core Web Vitals relies on 3 indicators:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) – measured in seconds
- FID (First Input Delay) – measured in milliseconds
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) – with values ranging from 0 to 1
According to Google, Good / Needs improvement / Poor status values of Core Web Vitals are falling into the following ranges:
Crawling
It’s the process through which search engines (like Google) browse websites with the scope to analyze and index their content. Today, crawling requires online content to be structured, coming from experts, trustworthy, and authoritative (promoted by Google’s search team as E-A-T ratings for many years already).
Crawling also is performed by SEO tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, Moz which browse websites (at your request) to analyze content and to check websites for errors. These tools can also perform competitive analysis, benchmarking your website content vs. competitors’.
E
E-A-T rating
In the digital dictionary, EAT is the acronym for “Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness”. It was launched by Google as “human rating guidelines” way back in 2013, in an effort to make its rating guidelines transparent.
Initially, it was more of an editorial guideline, but starting with 2018 Google algorithm updates, it became a critical factor for page quality scores, but also for Google ranking (although some SEO specialists still debate on that).
What do these three principles (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) stand for, and why are they important?
- Expertise: This principle means that the author(s) of the content on a website must prove they have expertise in that field. For example, on a website, the author (including the company) needs to have a name, picture, and detailed profile.
- Authoritativeness: This term refers basically to what authority requires – recognition, leadership. It’s what we expect in any source of information, whether is about news, health management, or legal advice.
- Trustworthiness: It assesses how believable the website, content, and author are all together. I would say that trustworthiness is the final objective for any piece of content indexed by Google.
As I was mentioned in a previous article, websites must be created for people, not rankings. For YMYL websites, focusing on getting high EAT ratings is critical, but this approach is in fact highly useful for non-YMYL sites, too.
The key-take-out here is that creating a user-centred website has far more chances of getting positively rated by Google’s search algorithm.
F
Featured snippets
Featured snippets are convenient, concise pieces of information (usually text) that offer an instant partial answer on Google search results page, without having to click anything nor to visit the target website.
Most of the time they precede the title of a website on the search results page.
Ahrefs estimated in an extensive study that 12.3% of search results have featured snippets.
Moreover, they determined that a website that ranks first and has also featured snippets can capture even 28.2% of all clicks from that search query.
However, I’ve seen that all these features are highly volatile, so as Google is changing display algorithms constantly, the figures above will vary significantly in the future.
FID (First Input Delay)
It represents the amount of time in milliseconds between a user’s request to view a page (e.g. by clicking a link) to the moment when the browser responds to that request.
The role of this KPI is to ensure that the websites are responsive enough to meet users’ speed expectations.
Good FID:
- <100ms
FID that needs improvement:
- <=300ms
Poor FID:
- >300ms
G
Google BERT
BERT is a natural language processing AI tool that makes Google understand the language better by taking into account its context.
“BERT” stands for “Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers”.
According to a Google spokesperson, BERT’s original name was DeepRank. DeepRank / BERT has been active in Google Search since October 2019.
Google Discover
Discover is a feed created by Google for mobile users. It is visible on Google’s iOS and Android mobile apps, but also on the mobile version of Google.com.
Just like with RSS feeds, users can create their own Discover feeds, based on their interests and preferences. The service is cost-free.
Google Search Console (GSC)
Search Console is an online tool that gathers and reports websites Search traffic and performance.
Its main features are performance reports, sitemap parsing, Google Discover, URL inspection, coverage reports, URL removals, disavow domains, Core Web Vitals, Mobile Usability, AMP, Breadcrumbs, Rich Snippets (like FAQ, Sitelinks searchbox) and other legacy tools and reports.
H
HTTP 1.1 protocol
It is a new type of web data protocol, which delivers web pages faster than the original HTTP version, managing at the same time to lower the amount of data traffic that is being transferred.
I
Indexing
It is the process through which a search engine stores information about a page, its content, structure, and relationships (called backlinks) with other pages.
The reversed process is called De-indexing and might happen when a page is deleted from the Google database (automatically or by users’ request) or when a website is banned by the search engine.
K
Keyphrase
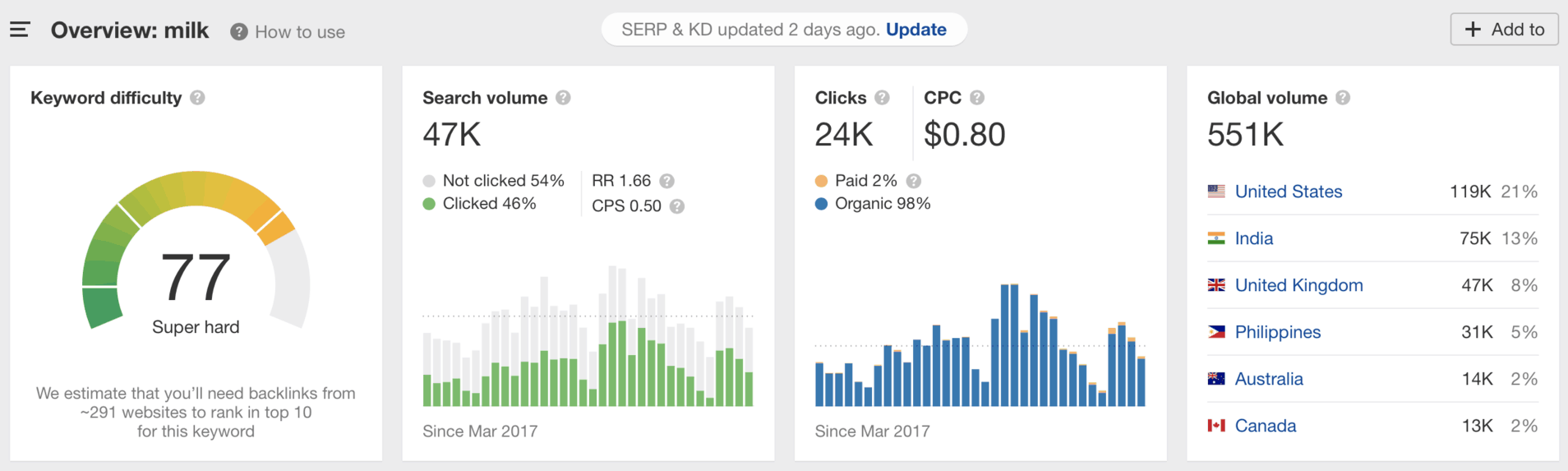
Keyphrases are combinations of keywords that are important to link user search intent (what people search in Google Search) with the theme of a website page.
When planning your content, you should always search for correspondent keyphrases with SEO tools or in Google Keywords Planner in order to increase your chances of being useful to users and to rank higher in Google Search.
Here’s an example of performing this keyword search in Ahrefs:
L
LCP (Largest Contentful Paint)
It measures how much time it takes a browser to render the largest content element that is visible in the viewport. The respective element can be a multimedia file (image, video), or a block of text. LCP is measured in seconds.
LCP is measured because users need visual confirmation that the respective page is loading on the respective device.
Good LCP:
- <2.5s
LCP that needs improvement:
- <=4s
Poor LCP:
- >4s
M
Meta Description
Meta Description is a list of text strings that indicate essentials elements of a page (what the page is about, author, last time the page was updated). They are very useful also for search engine users.
Sometimes these text fields are used by Google not only for listing in search but also to create rich snippets in SERP.
O
Organic vs. Non-organic
In SEO, organic relates to a website displayed in search results pages (SERP).
In contrast, when referring to Google Search, non-organic means paid advertisements.
P
Page Status Codes
There are four classes of page status codes:
- 2xx status codes: A class of status codes that indicate the request for a page has succeeded.
- 3xx status codes: They are redirection status codes, I just detailed them above, in the Redirection section.
- 4xx status codes: It’s a result following the request to browse a page or an element in a page (like an image, a video) that could not be found.
- 5xx status codes: They are server errors (such as “Server timeout”), that indicate browser requests that cannot be performed and usually affect the entire website. Most of the time these errors can be overcome only by web hosting specialists.
Preferred Domain
The preferred domain refers to the version of a website (that includes “www” before the domain name or not) of your domain that you want to be shown in the address bar of your browser and in search results.
As you see above, my preferred domain is https://stefanstroe.com (without the www) because I wanted to keep it shorter.
To Google, it doesn’t matter if you use a “www” or “non-www” domain (according to John Mueller, Webmaster Trends Analyst @Google).
In order to set your preferred domain, a redirection rule needs to be set on the server in order to avoid having published two versions of the website (with and w/o www) and any duplicated content problems red flags in Google. Additionally, you should set your preferred domain in Google Search Console.
Protocol (http, https, SSL)
The protocol is the prefix of a web domain name. It can be “HTTP” (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) or “HTTPS” (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure).
As you probably know, HTTPS protocol can be used only by installing an SSL (“Secure Sockets Layer”) certificate on your server, that manages to encrypt data between the end user’s device and your website’s server.
Q
Query
It is the technical term used by digital specialists that refers to the words that are being typed into a search field or search bar.
For example, during COVID-19 2020 crisis, people performed many interesting coronavirus related queries:

R
Redirection
It’s a written rule in the CMS or on the server (for example in cPanel Redirection section) when a URL has changed its location. In Technical SEO, redirection rules need to be set from the early beginning, but also continuously monitored.
There are five types of redirections:
- 301:Permanent Redirect (most commonly used). It tells crawlers to delete the old URL and to index the new one. Google recommends maintaining a 301 redirect in place for at least one year.
- 302: Temporary redirect. This redirect does not ask the web crawler to index the new URL, as the destination is temporary. A 302 redirect is commonly marked as a “Found” redirect.
- 303: It is also a temporary redirect like 302, but it tells crawlers not to cache the new address.
- 307: Similar to 303 and 302, the 307 redirection is newer, clearer instruction for crawlers that content was temporarily moved to a new location. It was introduced with the HTTP 1.1 protocol.
- 308: Permanent redirect
You can learn more about 3xx redirects in deepcrawl.com article.
Rich Results and Rich Snippets
With so many new words being invented in digital marketing and specialists debating about them, no wonder sometimes some people got to talk differently about the same things. It’s the case for Rich Results vs. Rich Snippets.
Is there any difference between these two? Well, yes, there is.
Rich Results
First, Rich Results is a general term, which includes all visual representations of search engine results pages (SERPs). Rich Snippets are one of them.
Rich Snippets
On the other hand, Rich Snippets are chunks of data (usually eye-catchy) that accompany a website listed in SERP besides its link, title, and meta description. See some of them in the image below.
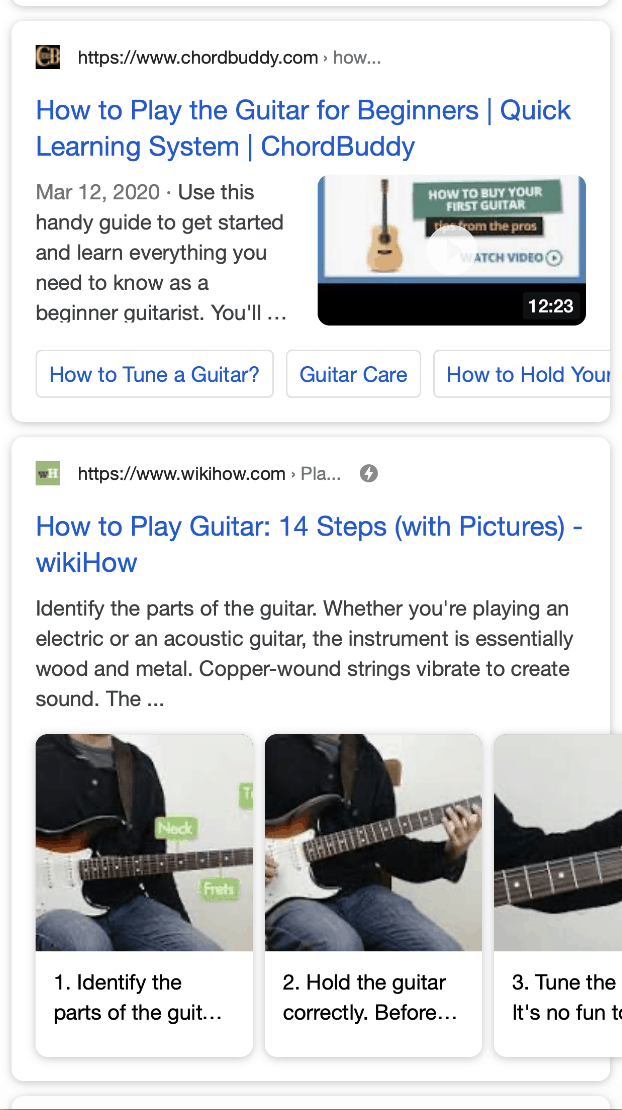
The reason Google introduced Rich Snippets is that it already managed to structure certain categories of data from the websites it indexed.
Because of the 8% extra clicks that they generate in the first SERP (according to Moz.com), today all SEO specialists work on their websites to generate as many Rich Snippets as possible.
Robots.txt
Robots are a set of rules uploaded in a website’s root directory that are mandatory for web crawlers, indicating which parts of the site they should crawl or not. It is a very important tool for both SEO and website security as it cannot be overlooked by malicious crawlers.
S
Search engine PPC (Pay-Per-Click ads)
PPC ads, in general, are advertisements for which and advertisers pay each time they are clicked by a visitor.
In Google Search, for example, they are called Google Ads (although many people still refer to them by their old name, “AdWords”) and as opposed to Organic Traffic, they work only if a campaign is active and has an allocated budget.
Search engine PPC ads are a form of Paid Search.
SEM (Search engine marketing)
It is a set of specific digital activities that have the main purpose of maximizing revenue through search engines.
Not many people know that SEM includes SEO with all its subsequent activities, but also PPC (Pay Per Click ads, such as Google ads), so this fact might be summarized in a memorable equation:
SEM = SEO + Search engine PPC
SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
SEO is an acronym for Search Engine Optimization, which includes a series of techniques and web editing processes that aim to acquire more free of charge, organic traffic via users’ search queries. It can be applied to any type of search engine, including Google, Bing, Yandex, YouTube, Pinterest, Instagram, and others.
For this SEO dictionary term, I recommend reading my previous article Top 5 questions on SEO with practical insights.
SERP (Search Engine Results Page)
Is the actual page with links of websites that a user sees in Google after performing a search query.
Important to say, most of the time SERP is different on desktop vs. mobile, very different from one location to another (and here Local SEO comes into play), but also based location on your activity.
For example, a logged-in Google Search Console manager might see a different SERP than a colleague searching the same term, even if they sit next to each other and that’s because Google is able to micro-personalize SERPs for each user.
SERP features
SERP features are content sections in Google Search results page that appear for some terms and which do not use the standard website page listing (title, short description, URL).
We could split them into 4 categories:
- Rich Snippets: Eye-friendly or useful elements such as prices, recipes, product ratings;
- Ads: In some countries besides AdWords users see products listed in Google Shopping, with image and price;
- General Snippets: Content that accompanies a website in search results: images, videos, featured snippets;
- Knowledge Graph: Sections that present data in a more intellectual way (e.g. knowledge card, aka graphs)
SERP features are spectacular and many times they receive more clicks than the website covering the first position. The most common examples are:
- Featured Snippets;
- Reviews (star ratings for products or content);
- Local Pack (info regarding nearby local businesses);
- Site Links (important sections of a website);
- Videos;
- Top Stories;
- FAQs (those clickable tabs with answers to questions, or “People also ask” sections).
You could read more about SERP features in this article from Semrush.
Sitemap
A Sitemap is a hierarchical, structured list of URLs of a website that is used by search engine crawlers in order to index its content. It’s a very important area of technical SEO.
Sitemaps can be customized to suit a website’s SEO needs. I am currently using WordPress and, in case you also use it, there are plenty of plugins to customize sitemaps, creating rules of including and excluding categories of items (pages, media items) or individual items from being indexed by Google. The most popular tools are Yoast SEO and RankMath which will help you also create automatic sitemaps.
That is why sitemap management is crucial for easing the discovery job of a search engine spider to perform a website inventory.
However, Google may discover content even if it’s not present in a site’s sitemap through internal links of a website (let’s not forget that crawlers check what’s beyond any working link, not only sitemap links).
As for the format, the most common sitemap format is XML, which Google understands best.
For example, my sitemap is here: https://stefanstroe.com/sitemap_index.xml
I have chosen what to be included in the sitemap based on the current content.
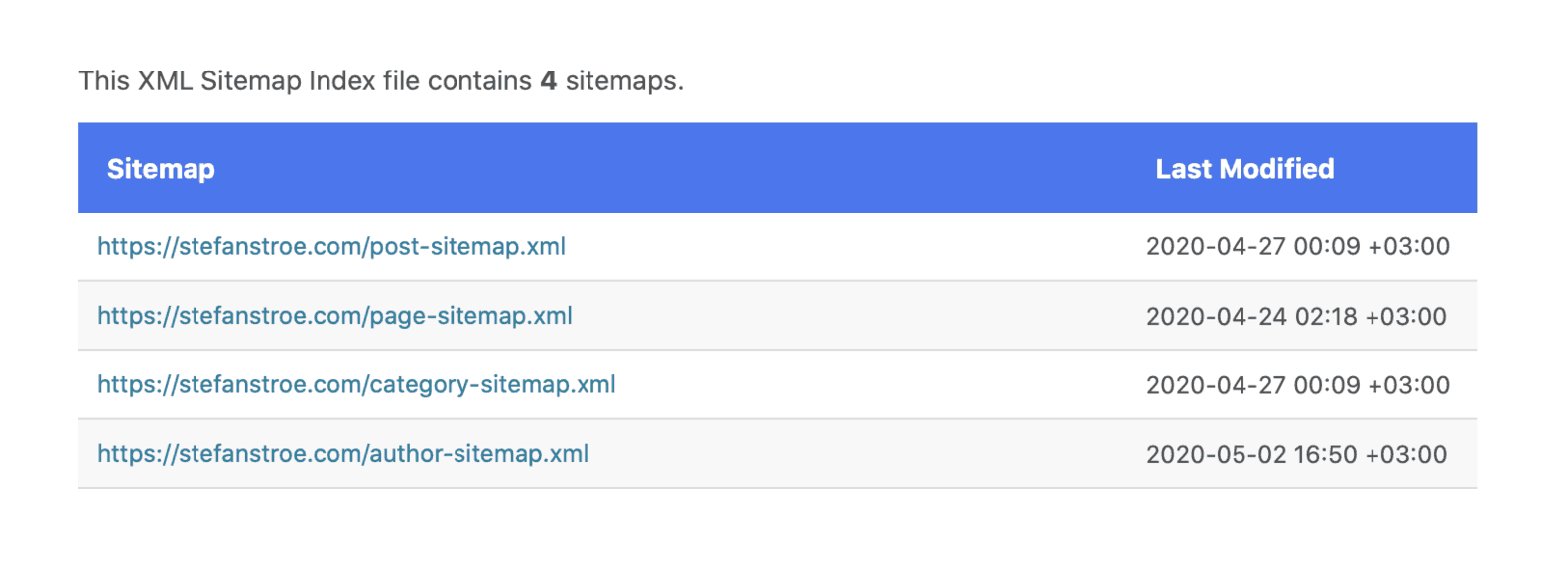
Spider / Web Crawler
They are programs behind search engines like Google that automatically and continuously browse the internet and fetch webpages.
It’s important to know that spiders/web crawlers are used also by SEO monitoring tools such as Ahrefs, Semrush, Moz, and others and if they are allowed by website servers, they can browse and analyze them (unlike Google by user request) for SEO purposes.
Structured data
I started this part of my SEO dictionary with the most important thing in user-centric SEO: Data Structure.
Google wrote many years ago that it aims to structure the information on the internet in the best possible way so that users could find their answers in the shortest time possible.
Google says in its guidelines:
For an SEO specialist, structured data means all the processes and tools he/she needs to use in order to comply with Google’s technical requirements for structuring their public website content.
Structured data is the core of many of the SEO dictionary terms below (SERP features, featured snippets, Rich Snippets, Rich Results), as they all are forms of structured data.
Structured data is so important for us that it has also its own testing tool: Structured Data Testing Tool.
In order to see what structured data it identifies, choose a website that has more than a title, link, and description in Google search results and test to see what Structured Data finds.
See an example from my work for the new Synevo.bg website, for laboratory test page:

Update November 2020: The structured data testing tool is outdated. To validate structured data, Google now recommends using the Rich Results tool.
T
Tags
Tags are elements in a website’s pages (visible or hidden to the user) that give search engine crawlers important hints on how to perform indexing or how to interpret certain important elements, like hyperlinks. Setting the right tags is critical for Technical SEO.
Here are the most important types of tags:
1. Title tag
The Title tag is an element written in HTML that marks in a page’s code which is its headline. It is a mandatory field for SEO.
2. Alt tag
The Alt tag is another important HTML attribute mandatory in SEO, which needs to be specified inside an IMG tag, helping the browser to display an “alternate text” in case an image can’t be shown.
3. Meta robots tags (or Meta Robots Directives)
Meta robots tags, called also Meta Robots Directives are chunks of code parameters that tell search engine spiders how to crawl elements of a page or the entire page itself.
How can we identify a meta robots tag in a page’s code?
<meta name=”robots” content=”[PARAMETER]”>
Unlike robots.txt instructions, meta robots tags can be overlooked by malicious web crawlers that intend to browse or copy your website’s content.
The most important parameters we usually set in a page are the following:
- Index: It’s a default parameter for any page, or link, which allows search engines to index the page. We do not have to set Index parameters.
- Follow: It’s a parameter that tells search engines to follow all the links on a page and add indexing importance to all of them.
- NoIndex: Tells search engines not to index that specific page.
- NoFollow: Tells search engines not to follow what’s behind a hyperlink in a website (starting 2020 it is a rule ignored by Google)
- NoImageIndex: As it says, it tells crawlers not to index images included on the page.
- Noarchive (“NoCache” in IExplorer & Firefox): Tells crawlers not to cache and hence not display in SERP that specific link.
- NoSnippet: Tells crawlers not to display rich results of that page in SERP.
- NoOpener: An parameter specific to WordPress, which is accompanied by a “NoReferrer” parameter in order to prevent malicious websites to exploit a specific security vulnerability.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO covers the list of activities that are performed outside content pages and is mostly related to the structure of a website.
Alongside On-page SEO and Off-page SEO, Technical SEO is focusing on getting a website to rank high in Google as fast as possible, without writing a single line of editorial content.
I added this technical area of search engine optimization in the SEO Dictionary is often overseen by top managers. Most times, managers judge Search Engine Optimization efforts mostly by looking at rankings in Google Search reports.
But especially in the developing stage, before publishing any website, an SEO specialist performs several technical steps in order to ensure proper indexing for the new website.
Some of these steps are performed straight in the file directory where the website is hosted, some require to edit website files (which usually require development skills), while some are completed in the admin area of the CMS (see for example WordPress Admin area).
U
URL: A forgotten term in SEO dictionary
So, to answer the question, the famous URL stands for Uniform Resource Locators. It’s not a fancy name, but it excels through its importance and role in our online life. As you already know, it refers to the unique addresses where individual pieces of content can be found on the web.
URL structure
URL structure is the policy set to structure the links on a website and it needs to be clearly set for both structuring the content database. A technical SEO specialist will always plan the URL structure before editing any content.
URL structure can include:
- Subdomains (not recommended for SEO) – format like https://SUBDOMAIN.website.com/
- Directories – format like https://stefanstroe.com/category/NAME-OF-CATEGORY/
- Subdirectories – see an example of my multilingual URL structure: https://stefanstroe.com/LANGUAGE/CATEGORY/
- Query strings – some websites add query strings parameter at the end of a page URL: https://shop.com/product-name?name=sweater&size=2
User Experience (UX)
It is a digital marketing concept derived from the more broad term called “Customer Experience” (CX) and comprises the results of the encounter between a person (user) and a brand property (website, app, social account, physical device, branded content etcetera).
User Experience (UX) is a prominent term in the SEO Dictionary because it shapes many search engine optimization decisions, such as:
- improving websites’ speed and responsiveness
- designing and updating content
- monitoring user search intent.
User intent
User intent is not a typical SEO Dictionary term, although it should be the purpose of search engine optimization.
As I mentioned a bit earlier explaining White hat SEO, “user intent” refers to the principle which Google intensively promotes for a few years already: Digital content should be written or produced for the user.
For this reason, Google Search AI capabilities improved significantly in late 2019 with the BERT neural network-based technique for natural language processing (NLP), so all content publishers will have to comply more and more with this principle if they intend to rank high in Google.
W
Webmaster Tools
It is a tool that allows webmasters (site administrators) to verify how their websites are indexed by search engines. In May 2015 Google renamed its “Webmaster Tools” as “Google Search Console”. Currently, Yandex calls this service “Yandex.Webmaster” while Bing calls it by the generic name, “Webmaster Tools”.
White hat SEO
It is the optimization performed with the human user in mind and it’s an important term in the SEO Dictionary. It follows the search engines’ guidelines and as Google recommends, white hat SEO should be performed with users’ search intent in mind (similar to how retailers are focused on building great customer experience).
If you are interested in using or paying for SEO, I think you should go first through Google’s Search Quality Rating Guidelines, the ‘bible’ of mastering white hat SEO.
Y
YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) websites
Google created a special category of websites for which sometimes create targeted search algorithm updates.
In this category are included all financial, medical, and legal websites. Important to know, this isn’t only about company-owned sites, but also private ones.
Web pages of individuals that offer professional or qualified advice regarding health, money, or life management are automatically included in YMYL.
For these sites, Google set a special set of rules for assessing content quality, which is called E-A-T ratings (detailed below). As discriminatory as this sounds, this set of rules makes sense given the importance of YMYL websites.
YMYL is a wider concept than thought initially but deserves its place in this SEO Dictionary, as now it covers also all web stores that have payment gateways in their checkout pages.